In Germany, GMO-free regions and initiatives are being founded by conventional and organic farmers. By signing contracts – negotiated agreements – they are expressing their commitment among each other not to grow genetically modified plant on their farmland. The commitment can be expanded to include GMO-free animal feed.
 Allen Bäuerinnen und Bauern steht es frei, eine Gentechnikfreie Region zu gründen.
(Jerzy Gorecki
/
pixabay.com)
Allen Bäuerinnen und Bauern steht es frei, eine Gentechnikfreie Region zu gründen.
(Jerzy Gorecki
/
pixabay.com)
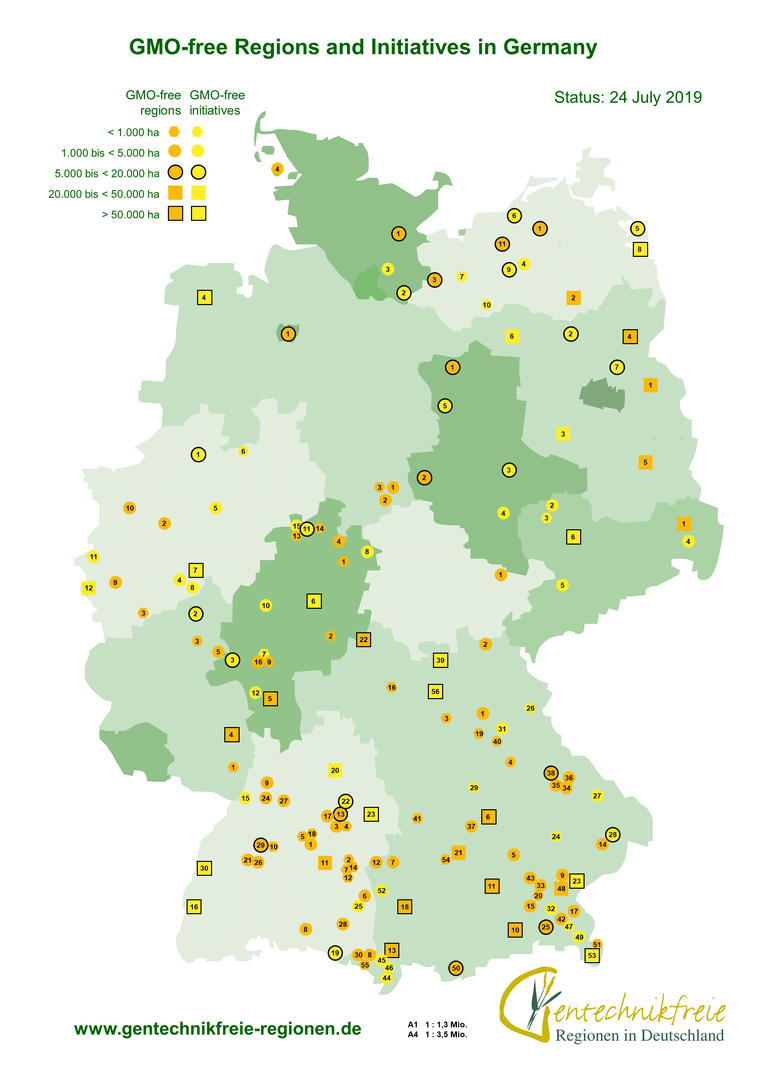
What is a GMO-free region?
In case the GMO-free farmland in the chosen reference area (e.g. a district) adds up to a surface coverage of two-thirds and above, the farmers established a so called GMO-free region. If this coverage is not yet met, the term GMO-free initiative applies.
The first GMO-free region in Germany was founded in 2003. In the meanwhile, about 33,000 farmers on approximately 1.3 million hectares farmland are organized in 215 GMO-free regions and initiatives. In other words: More than 10% of German farmland is declared GMO-free and approximately 9% of all German farmers confirm their anti-GMO attitude.
| Number | Area in hectares (reference area in hectares) | Number of farmers involved | Extend of contract | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GMO-free regions | 121 | 831.388 (1,698,230) | 23,787 | 96x Cultivation, 25x Cultivation and animal feed |
| GMO-free initiatives | 94 | 351.340 (1,892,973) | 8,173 | 45x Cultivation, 49x Cultivation and animal feed |
| GMO-free regions and initiatives | 215 | 1,182,728 (3,591,203) | 31,960 | 141x Cultivation, 74x Cultivation and animal feed |
| Individual declaration of farmers (not part of a gmo-free initiative or region) | 1,158 | 79,623 | 1,158 | |
| GMO-free agriculture in total | 1,262,351 (3,670,826) | 33,118 |
German fields are GMO-free
Monsanto’s MON 810 maize is banned since 2009. BASF’s Amflora potato was an economic disaster from the very beginning: Authorized in 2010 for cultivation, it was grown just by one farmer on 15 hectares in 2010 and lastly 2 hectares in 2011. In December 2013, Amflora’ s authorization for cultivation was withdrawn EU-wide by the European General Court (EGC). In addition, the number of field trials is continuously dropping: from 67.8 hectares in 2007 (peak) to 0.8 hectares in 2012 to zero in 2013/2014.
The movement of GMO-free regions is a strong signal to the biotech industry that German farmers are no potential clients.
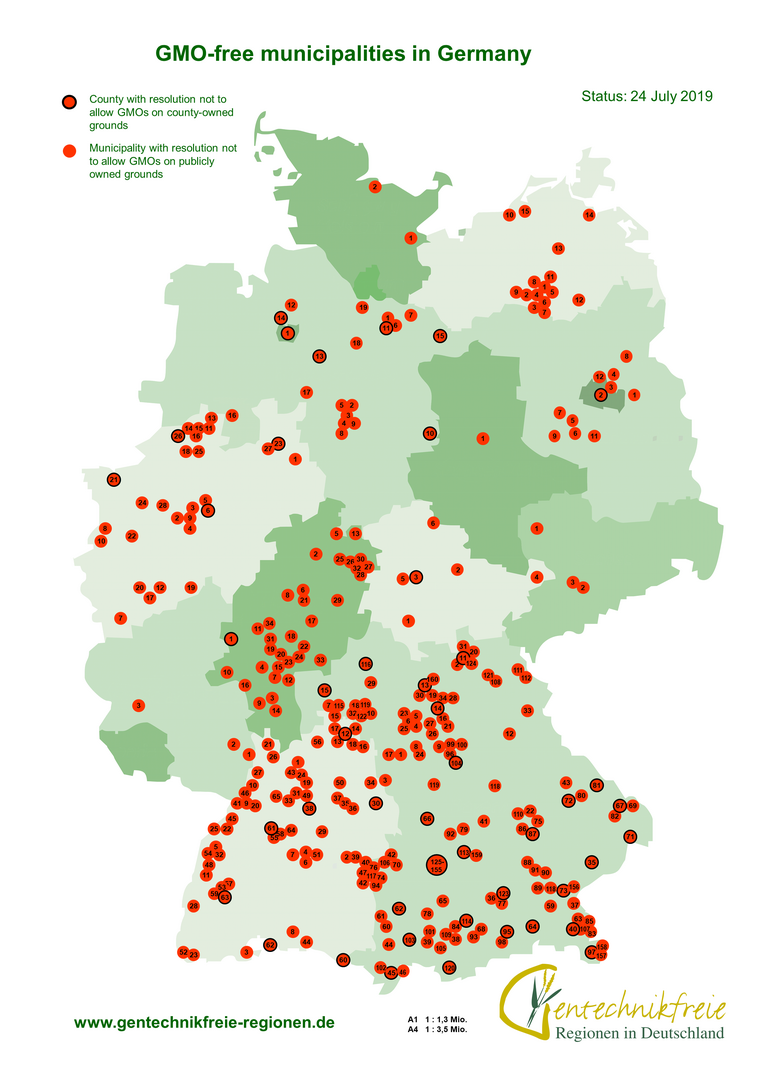
GMO-free municipalities
Landowners such as municipalities, towns and districts can forbid the use of genetically modified plants on their farmland. By adding a passage in the lease contract which prohibits the use of GMOs, they can legally oblige farmers to exclude GMOs on publicly-owned land.
In 1999, Munich was the first town that excluded GM plants from their properties. By now, more than 350 municipalities have followed this example.
The main arguments for GMO-free municipalities are:
- GM plants reduce land value.
- GM plants are against the will of farmers and consumers.
By prohibiting GMOs on their land the municipalities stand in for a regional and traditional agriculture. Farmers often follow GMO-free municipalities by founding GMO-free regions and vice-versa.